Nonmetals called chemical elements that form simple substances in their free form, they do not have the physical properties of metals. Of the 109 chemical elements, 87 can be attributed to metals, 22 are non-metals.
Under normal conditions, non-metals can be found in gaseous, liquid, and solid state.
gases are helium He, neon Ne, argon Ar, krypton Kr, xenon Xe, radon Rn. This is all inert gases. Each inert gas molecule consists of one atom. At the outer electronic level, atoms of inert gases (except helium) have eight electrons. Helium has only two. Due to their chemical stability, inert gases can be compared with noble precious metals - gold and platinum, they also have another name - noble gases. A similar name is better suited to inert gases, since they can enter into chemical reactions and form chemical compounds. In 1962, it became known that xenon and fluorine could form compounds. Since that time, more than 150 chemical compounds of xenon, krypton, radon with fluorine, oxygen, chlorine and nitrogen have been known.
The idea of the chemical exclusivity of noble or inert gases turned out to be not entirely correct, therefore, instead of the expected zero group, inert gases were assigned to the eighth group of the Periodic system.
Gases such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, chlorine and fluorine form diatomic molecules, already familiar to us H 2, O 2, N 2, CL 2, F 2.
The composition of a substance can be expressed using chemical and mathematical signs - a chemical formula. As we already know, the relative molecular weight of a substance (Mr) can be calculated from the chemical formula. The relative molecular mass of a simple substance is equal to the product of the relative atomic mass by the number of atoms in a molecule, for example, oxygen: O 2
Mr (O 2) \u003d Ar (O) 2 \u003d 16 2 = 32
However, oxygen can form another gaseous elementary substance - ozone, the composition of the ozone molecule already includes three oxygen atoms. Chemical formula O 3 .
The ability of atoms of one chemical element to create several simple substances is called allotropy, and these simple substances - allotropic changes, they are also called modifications.
The properties of allotropic modifications of the chemical element oxygen: simple substances O 2 and ozone O 3 differ significantly.
Oxygen does not have a characteristic odor, unlike ozone (hence the name ozone came from - translated from Greek, ozone means "smelling"). A similar aroma can be felt during a thunderstorm, the gas is formed in the air due to electrical discharges.
Oxygen has no color, unlike ozone, which can be distinguished by its pale purple hue. Ozone has bactericidal properties. It is also used for disinfection drinking water. Ozone can interfere with the passage of ultraviolet rays of the solar spectrum, they are detrimental to all living organisms on Earth. The ozone screen (layer), which is located at an altitude of 20-35 km, protects all living things from the harmful rays of the sun.
From 22 simple non-metal substances under normal conditions in liquid state, only bromine exists, its molecules are diatomic. Bromine's formula: Br 2 .
Bromine is a heavy brown bad smell liquid (bromos from the ancient Greek language is translated as "stinking").
Non-metal solids such as sulfur and carbon have been known since ancient times (charcoal).
Solid non-metal substances are also prone to the phenomenon of allotropy. Carbon can form such simple substances as diamond, graphite, etc. The difference in the structure of diamond and graphite lies in the structure of crystal lattices.
Do you have any questions? Don't know how to do your homework?
To get the help of a tutor - register.
The first lesson is free!
www.site, with full or partial copying of the material, a link to the source is required.
MNOU "Lyceum"
Essay on chemistry on the topic:
"Nonmetals"
Completed:
11 "A" class students
Kucherenko Maria,
Shadrina Xenia.
Checked:
chemistry teacher
Shcherbakova Marina
Alexandrovna.
Kemerovo - 2002
Introduction……………………………………………………………………..3
§1. The position of non-metallic elements in the periodic system of chemical elements. Finding in nature. General chemical and physical properties……………………………………4
§2. Are common Chemical properties non-metals………………………..6
§3. The structure and properties of simple substances - non-metals………7
§4. Oxygen and hydrogen compounds of non-metals. Brief description of their properties………………………………………………9
Test
List of used literature
Introduction .
All the diversity of nature around us consists of combinations of a relatively small number of chemical elements.
In different historical epochs, different meanings were put into the concept of “element”. Ancient Greek philosophers considered four "elements" as "elements" - heat, cold, dryness and humidity. Combining in pairs, they formed the four "origins" of all things - fire, air, water and earth. In the Middle Ages, salt, sulfur and mercury were added to these principles. In the 17th century, R. Boyle pointed out that all elements are of a material nature and their number can be quite large.
In 1787, the French chemist A. Lavoisier created the "Table of Simple Bodies". It included all the elements known by that time. The latter were understood simple bodies, which could not be decomposed by chemical methods into even simpler ones. Subsequently, it turned out that some complex substances were included in the table.
At present, the concept of "chemical element" is established precisely.
A chemical element is a set of atoms with the same positive charge on the nucleus. (The latter is equal to the ordinal number of the element in the periodic table.)
Currently, 107 elements are known. About 90 of them exist in nature. The rest are obtained artificially using nuclear reactions. Elements 104-107 were synthesized by physicists at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research in Dubna. Work is currently ongoing on artificial obtaining chemical elements with higher ordinal elements.
All elements are divided into metals and non-metals. Of the 107 elements, 85 are metals. Non-metals include the following elements: helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, radon, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, astatine, oxygen, sulfur, selenium, tellurium, nitrogen, phosphorus, arsenic, carbon, silicon, boron, hydrogen. However, this division is conditional. Under certain conditions, some metals may exhibit non-metallic properties, and some non-metals may exhibit metallic properties.
§1. The position of non-metallic elements in the periodic system of chemical elements. Finding in nature. General chemical and physical properties.
There are relatively few non-metallic elements compared to metallic elements. Their placement in the periodic system of chemical elements D.I. Mendeleev is reflected in table No. 1.
Table number 1.
As can be seen from table No. 1, non-metallic elements are mainly located in the upper right part of the periodic table. Since in periods from left to right the charges of the nuclei of the atoms of the elements increase and the atomic radii decrease, and in the groups from top to bottom the atomic radii also increase, it is clear why the outer electrons attract the non-metal atom more strongly than the metal atoms. In this regard, non-metals are dominated by oxidizing properties. Particularly strong oxidizing properties, i.e. the ability to attach electrons is shown by non-metals that are in the 2nd and 3rd periods of groups VI-VII. Fluorine is the strongest oxidizing agent. In accordance with the numerical values of the relative electronegativities, the oxidative abilities of non-metals increase in the following order: Si, B, H, P, C, S, I, N, Cl, O, F. Therefore, fluorine interacts most vigorously with hydrogen and metals:
Oxygen reacts less vigorously:
Fluorine is the most typical non-metal, which is uncharacteristic restorative properties, i.e. the ability to donate electrons in chemical reactions.
Oxygen, judging by its compounds with fluorine, can also exhibit a positive oxidation state, i.e. be a restorer.
All other non-metals exhibit reducing properties. Moreover, these properties gradually increase from oxygen to silicon: O, Cl, N, I, S, C, P, H, B, Si. So, for example, chlorine does not combine directly with oxygen, but its oxides can be obtained indirectly (Cl2 O, ClO2, Cl2O2), in which chlorine exhibits a positive oxidation state. Nitrogen at high temperatures directly combines with oxygen and, therefore, exhibits reducing properties. Sulfur reacts even more easily with oxygen: it also exhibits oxidizing properties.
Let us turn to the consideration of the structure of non-metal molecules. Non-metals form both monatomic and diatomic molecules.
Monatomic non-metals include inert gases that practically do not react even with the most active substances. Inert gases are located in Group VIII of the Periodic Table, and the chemical formulas of the corresponding simple substances are as follows: He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe and Rn.
Some non-metals form diatomic molecules. These are H2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2 (elements of the VII group of the Periodic system), as well as oxygen O2 and nitrogen N2. Ozone gas (O3) consists of triatomic molecules.
For non-metal substances that are in the solid state, it is quite difficult to make a chemical formula. The carbon atoms in graphite are connected to each other in various ways. It is difficult to isolate an individual molecule in the given structures. When writing the chemical formulas of such substances, as in the case of metals, the assumption is introduced that such substances consist only of atoms. Chemical formulas, in this case, are written without indices - C, Si, S, etc.
Such simple substances as ozone and oxygen, which have the same qualitative composition (both consist of the same element - oxygen), but differ in the number of atoms in the molecule, have different properties. So, oxygen has no smell, while ozone has a pungent smell that we feel during a thunderstorm. The properties of solid non-metals, graphite and diamond, which also have the same qualitative composition but different structure, differ sharply (graphite is brittle, diamond is hard). Thus, the properties of a substance are determined not only by its qualitative composition, but also by how many atoms are contained in a substance molecule and how they are interconnected.
Non-metals in the form of simple bodies are in a solid or gaseous state (excluding bromine - liquid). They do not have the physical properties of metals. Solid non-metals do not have the characteristic luster of metals, they are usually brittle, poorly conduct electricity and heat (with the exception of graphite).
§2. General chemical properties of non-metals.
Non-metal oxides are classified as acidic oxides, which correspond to acids. Non-metals form gaseous compounds with hydrogen (eg HCl, H2S, NH3). Aqueous solutions of some of them (for example, hydrogen halides) are strong acids. With metals, typical non-metals give compounds with ionic bonds (eg NaCl). Non-metals can, under certain conditions, react with each other, forming compounds with covalent polar (H2O, HCl) and non-polar bonds (CO2).
Non-metals form volatile compounds with hydrogen, such as hydrogen fluoride HF, hydrogen sulfide H2S, ammonia NH3, methane CH4. When dissolved in water, the hydrogen compounds of halogens, sulfur, selenium and tellurium form acids of the same formula as the hydrogen compounds themselves: HF, HCl, HCl, HBr, HI, H2S, H2Se, H2Te.
When ammonia is dissolved in water, ammonia water is formed, usually denoted by the formula NH4OH and called ammonium hydroxide. It is also denoted by the formula NH3 H2O and is called ammonia hydrate.
With oxygen, non-metals form acidic oxides. In some oxides, they exhibit a maximum oxidation state equal to the group number (for example, SO2, N2O5), while in others, a lower one (for example, SO2, N2O3). Acid oxides correspond to acids, and of the two oxygen acids of one non-metal, the one in which it exhibits a higher degree of oxidation is stronger. For example, nitric acid HNO3 is stronger than nitrous HNO2, and sulfuric acid H2SO4 is stronger than sulphurous H2SO3.
§3. The structure and properties of simple substances - non-metals.
The most typical non-metals have a molecular structure, while the less typical ones have a non-molecular structure. This explains the difference in their properties. This is clearly shown in Figure 2.
Table number 2
Crystalline boron B (like crystalline silicon) has a very high melting point (2075°C) and high hardness. The electrical conductivity of boron increases greatly with increasing temperature, which makes it possible to widely use it in semiconductor technology. The addition of boron to steel and alloys of aluminum, copper, nickel, etc. improves their mechanical properties.
Borides (compounds of boron with certain metals, such as titanium: TiB, TiB2) are necessary in the manufacture of jet engine parts, gas turbine blades.
As can be seen from scheme No. 2, carbon C, silicon Si, boron B have a similar structure and have some common properties. As simple substances, they occur in two modifications - crystalline and amorphous. The crystalline modifications of these elements are very hard, with high temperatures melting. Crystalline silicon has semiconductor properties.
All these elements form compounds with metals - carbides, silicides and borides (CaC2, Al4C3, Fe3C, Mg2Si, TiB, TiB2). Some of them have higher hardness, such as Fe3C, TiB. Calcium carbide is used to produce acetylene.
If we compare the arrangement of electrons in orbitals f atoms of fluorine, chlorine and other halogens, then we can also judge their distinctive properties. The fluorine atom has no free orbitals. Therefore, fluorine atoms can only show valence I and oxidation state - 1. In the atoms of other halogens, for example, in the chlorine atom, there are free d-orbitals at the same energy level. Due to this, the depairing of electrons can occur in three different ways.
In the first case, chlorine can show an oxidation state of +3 and form hydrochloric acid HClO2, which corresponds to salts - chlorites, for example, potassium chlorite KClO2.
In the second case, chlorine can form compounds in which the oxidation state of chlorine is +5. These compounds include chloronic acid HClO3 and its salts - chlorates, for example, potassium chlorate KClO3 (Bertolet's salt).
In the third case, chlorine exhibits an oxidation state of +7, for example, in perchloric acid HClO4 and in its salts - perchlorates, for example, in potassium perchlorate KClO4.
§4. Oxygen and hydrogen compounds of non-metals. Brief description of their properties.
With oxygen, non-metals form acidic oxides. In some oxides, they exhibit a maximum oxidation state equal to the group number (for example, SO2, N2O5), while in others, a lower one (for example, SO2, N2O3). Acid oxides correspond to acids, and of the two oxygen acids of one non-metal, the one in which it exhibits a higher degree of oxidation is stronger. For example, nitric acid HNO3 is stronger than nitrous HNO2, and sulfuric acid H2SO4 is stronger than sulphurous H2SO3.
Characteristics oxygen compounds of non-metals:
1. Properties higher oxides(i.e. oxides, which include an element of this group with the highest oxidation state) in periods from left to right gradually change from basic to acidic.
2. In groups from top to bottom, the acidic properties of higher oxides gradually weaken. This can be judged by the properties of the acids corresponding to these oxides.
3. The increase in the acidic properties of the higher oxides of the corresponding elements in periods from left to right is explained by a gradual increase in the positive charge of the ions of these elements.
4. In the main subgroups of the periodic system of chemical elements in the direction from top to bottom, the acidic properties of higher oxides of non-metals decrease.
The general formulas of hydrogen compounds according to the groups of the periodic system of chemical elements are given in table No. 3.
Table number 3.
With metals, hydrogen forms (with a few exceptions) non-volatile compounds, which are non-molecular solids. Therefore, their melting points are relatively high.
With non-metals, hydrogen forms volatile compounds of a molecular structure. Under normal conditions, these are gases or volatile liquids.
In periods from left to right, the acidic properties of volatile hydrogen compounds of non-metals in aqueous solutions are enhanced. This is due to the fact that oxygen ions have free electron pairs, and hydrogen ions have a free orbital, then a process takes place that looks like this:
H2O + HF - H3O + F
Hydrogen fluoride in an aqueous solution splits off positive hydrogen ions, i.e. exhibits acidic properties. Another circumstance also contributes to this process: the oxygen ion has an unshared electron pair, and the hydrogen ion has a free orbital, due to which a donor-acceptor bond is formed.
When ammonia is dissolved in water, the opposite process occurs. And since nitrogen ions have an unshared electron pair, and hydrogen ions have a free orbital, an additional bond arises and ammonium ions NH4 + and hydroxide ions OH- are formed. As a result, the solution acquires basic properties. This process can be expressed by the formula:
H2O + NH3- NH4 + OH
Ammonia molecules in an aqueous solution add positive hydrogen ions, i.e. ammonia exhibits basic properties.
Now consider why the hydrogen compound of fluorine - hydrogen fluoride HF - in an aqueous solution is an acid, but weaker than hydrochloric acid. This is due to the fact that the radii of fluorine ions are much smaller than those of chlorine ions. Therefore, fluorine ions attract hydrogen ions much more strongly than chloride ions. In this regard, the degree of dissociation of hydrofluoric acid is much less than that of hydrochloric acid; hydrofluoric acid is weaker than hydrochloric acid.
From the examples given, the following can be made general conclusions:
1. In periods from left to right, the positive charge of the ions of the elements increases. In this regard, the acidic properties of volatile hydrogen compounds of elements in aqueous solutions are enhanced.
2. In groups, from top to bottom, negatively charged anions attract more and more weakly positively charged hydrogen ions H+. In this regard, the process of splitting off hydrogen ions H + is facilitated and the acidic properties of hydrogen compounds increase.
3. Hydrogen compounds of non-metals, which have acidic properties in aqueous solutions, react with alkalis. Hydrogen compounds of non-metals, which have basic properties in aqueous solutions, react with acids.
4. The oxidizing activity of hydrogen compounds of non-metals in groups from top to bottom increases greatly. For example, it is impossible to oxidize fluorine from the hydrogen compound HF chemically, but chlorine can be oxidized from the hydrogen compound HCl by various oxidizing agents. This is explained by the fact that atomic radii sharply increase from top to bottom in groups, in connection with which the return of electrons is facilitated.
List of used literature.
1. Rudzitis G.E., Feldman F.G. Chemistry-11 - M .: Education, 1992.
2. Kremenchugskaya M., Vasiliev S. Schoolchildren's Handbook - M.: AST, 1999.
3. Khomchenko G.P. Chemistry for applicants to universities - M .: Higher School, 1993.
NON-METALS, chemical elements that do not have the properties characteristic of metals. Non-metals are generally poor conductors of heat and electricity (they are usually insulators of heat and electricity). Non-metals include carbon, ... ... Scientific and technical encyclopedic dictionary
Chemical elements, which form simple bodies that do not have the properties characteristic of metals. Non-metals usually include 22 elements: gases hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine and noble gases; liquid bromine; solid bodies boron, ... ... Big Encyclopedic Dictionary
NON-METALS- chem. elements that form in the free state simple substances that do not have physical. and chem. properties (see); obsolete name for a metalloid. It is customary to refer to N. 22 elements of the Periodic Table of Elements of D. I. Mendeleev (see): hydrogen ... Great Polytechnic Encyclopedia
Chemical elements that form simple bodies that do not have the properties characteristic of metals. Non-metals usually include 22 elements: gases hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine and noble gases; liquid bromine; solid bodies boron, ... ... encyclopedic Dictionary
non-metals- chemical elements that form simple bodies that do not have the properties characteristic of metals. Non-metals include 22 elements. Of these, at room temperature are in the gaseous state H, N, O, F, Cl ... Encyclopedic Dictionary of Metallurgy
Chemical elements that form simple bodies that do not have the properties characteristic of metals (See Metals). The name Metalloids, which is sometimes used for N., is falling into disuse. N. includes 22 elements. Of these, with ... ... Great Soviet Encyclopedia
Simple in va, not possessing your metals. Although it is impossible to draw a sharp line between metals and nitrogen, noble gases, hydrogen, halogens, oxygen, chalcogens, nitrogen, phosphorus, arsenic, carbon, silicon, and boron are commonly referred to as nitrogen. Big encyclopedic polytechnic dictionary
Chem. elements that form simple bodies that do not have the properties characteristic of metals. To N. usually carry 22 elements: gases hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine and noble gases; liquid bromine; tv. bodies boron, carbon, silicon, phosphorus, ... ... Natural science. encyclopedic Dictionary
NON-METALS- simple substances that do not have the properties of metals: they do not have a metallic luster, non-forging, poorly conduct heat and electricity. There is no sharp boundary between non-metals and metals. Non-metals include 22 elements. Of these, under normal ... ... Metallurgical Dictionary
Inorganic chemistry is a branch of chemistry associated with the study of the structure, reactivity and properties of all chemical elements and their inorganic compounds. This area covers all chemical compounds, with the exception of organic ... ... Wikipedia
Books
- A set of tables. Chemistry. Non-metals (18 tables), . Educational album of 18 sheets. Art. 5-8688-018 Halogens. Chemistry of halogens. Sulfur. Allotropy. Chemistry of sulfur. Sulfuric acid. Chemistry of nitrogen. nitrogen oxides. Nitric acid is an oxidizing agent. Phosphorus.…
- Chemistry. Metals. Nonmetals. Grade 9 Workbook, Koroshchenko Antonina Stepanovna. Workbook contains a large number of tasks that can be used to achieve subject, meta-subject and personal results of teaching chemistry in grade 9. Benefit…
- Chemistry tests: 9 cells. : Nonmetals. Generalization of knowledge in chemistry for the course of the basic school. Preparation for the Basic State Exam. Federal State Educational Standard, Ryabov, Mikhail Alekseevich. This manual fully complies with the federal state educational standard (second generation). The manual includes tests covering two topics of the textbook by O. S. Gabrielyan ...
Among simple substances, some differ in a number of common features. They have a characteristic brilliance, malleability, conduct electric current well. Such simple substances are called metals(Fig. 11.3), and the corresponding chemical elements - metal elements. All metals have a non-molecular structure. One of the most important metals is iron.
Table. Some metals, products from them and mention in the literature
|
Au Golden pectoral (detail) |
The roar subsided, and the glow faded, Only gold shines with the sun, The wind whistles over the blue steppe The name of the Scythian glorifies. Boris Mozolevsky. Scythian steppe |
|
Al Aluminum products  |
The sculpture "Eros" in Piccadilly Circus in London, UK is one of the first sculptures in the manufacture of which aluminum was used. |
|
Cu Copper weather vane  |
Copper, like gold, differs from other metals in its characteristic color. And a copper mortar, red copper, only the pestle is broken ... Ivan Karpenko Kary. One hundred thousand So Svyatoslav's mother, Princess Olga, approached Svyatoslav, she was holding in her hands a work made by the best blacksmiths from red copper, gilded, decorated with many precious stones helmet. Semyon Sklyarenko. Svyatoslav |
|
hg Mercury under standard conditions (t\u003d 25 ° С, P \u003d 1 atm) - liquid  |
And for several sazhens around the boat, a heavy, motionless, like mercury, dead swell was dull silver. Chingiz Aitmatov. Piebald dog running along the edge of the sea |
|
Ag silver coins  |
Blessed is the man who has gained wisdom, and the man who has gained understanding, because gaining it is better than gaining silver. Ivan Ohienko. Bible |
|
Zn Galvanized tableware  |
Oh, how many, how many May puddles - Scraps of blue zinc! Vasily Kazin. Working May The pond is lined with zinc along the edges, and once a week this zinc is removed, taken to the kitchen, where it is scrubbed to a shine. Jerome K. Jerome. Three on bicycles / Translated by A. Popov |
Nonmetalsproperties characteristic of metals are not inherent. Nevertheless, there is no clear boundary between these groups of substances.material from the site
For example, silicon- non-metal. However, in appearance it is easy to confuse it with metal. Silicon is widely used as a material for the manufacture of semiconductor devices, wafers for solar energy systems. Non-metal graphite, like metals, conducts electricity.
Non-metals correspond non-metallic chemical elements.
Carbon, sulfur, phosphorus, oxygen, nitrogen, chlorine, bromine and iodine are classified as non-metals. Chlorine is a gas. Bromine is a volatile liquid. Iodine crystals have characteristic color and brilliance, which make it somewhat similar to metals. When heated, iodine forms violet vapors.
Non-metals are predominantly made up of molecules. However diamond(simple carbon matter) and silicon- Substances of atomic structure.
The names of metals and non-metals are common nouns, not their own.
How to find out from the periodic table whether a chemical element is metallic or non-metallic? There are much fewer non-metallic elements. Predominantly, they are located on the right side of the periodic table. Their cells are marked with bold lines.
On this page, material on the topics:
Chemistry cheat sheet metals and non-metals
Message on metals and non-metals
Metals and non-metals chemistry report
School report - non-metals
What is metal and non-metal gdz
Questions about this item:
Studying the paragraph will help you:
give examples of simple substances of metals and non-metals;
Distinguish between metals and non-metals, metallic and non-metallic elements;
· use the periodic system as a reference to determine the placement of some non-metallic and metallic chemical elements in it.
WHAT SUBSTANCES TO POUR TO SIMPLE? A feature of any science is that the objects under study are subject to classification. Chemical science is no exception, because substances cannot be studied without proper classification.
According to the qualitative composition, substances are divided into simple and complex.
Simple substances are substances formed by atoms of one chemical element
In the above list of formulas: Fe, O 2, H 2 O, NaHCO 3, NaCl, H 2 SO 4, N 2, Al 2 O 3, Al, O 3 we find the formulas of simple substances. Using the above definition of simple substances, we conclude that these will be the formulas: Fe, O 2, N 2, Al, B 3. Other formulas are formed from atoms of different chemical elements. As you know from natural science, these are complex substances.
Atoms of one chemical element can form several simple substances. For example, oxygen atoms O 2 and ozone consist of oxygen atoms; their chemical formulas differ in the number of oxygen atoms. This is exactly what is shown in Figure 55.
Rice. 55. Models of oxygen molecules (a) and ozone (6)
* Separation of something according to certain characteristics.

Rice. 56. Diamond (a) and graphite (c) and models of their structure (6. d)
Carbon atoms formed the hardest natural substance diamond, and so soft that it leaves inscriptions on paper - graphite. The chemical formulas of these substances are written in the same way - C. Differences in the properties of diamond graphite are due not to different quantitative or qualitative composition, but to different spatial arrangement of carbon atoms in the substance relative to each other (Fig. 56). In graphite, they are placed in layers, and the distances between atoms within one layer are much less than between adjacent layers (Fig. 56d). Therefore, it is enough to lightly press the pencil and the integrity between the layers is violated. In diamond, carbon atoms are arranged in such a way that they are at the same distance from each other, and the bonds between them are directed towards the vertices of the tetrahedron (Fig. 56b). This causes a high hardness of the substance.
Despite the examples given, think about which is more - chemical elements or simple substances.
According to the modern Ukrainian chemical nomenclature, the names of some simple substances do not coincide with the names of the chemical elements from which they were formed. The table shows examples of such substances. Get to know them.
Find in the table and write down in a notebook the names and formulas of simple substances. in which the molecule is formed by two or more atoms.
Table 4
Formulas and names of simple substances
|
simple substance |
Name of the chemical element |
simple substance |
Name of the chemical element |
||
|
Name |
Name |
||||
|
Argentum |
|||||
|
oxygen |
|||||
|
Mercury |
graphite, diamond |
||||
Note! The names of simple substances are written with a small letter, the names of chemical elements - with a capital letter.
METALS AND NON-METALS. Simple substances are divided into metals and non-metals. Metals include zinc Zn, potassium K, calcium Ca, magnesium Mg, tin Sn, lead Pb, copper Cu, iron Fe, aluminum Al, silver Ag, gold Au and others (Fig. 57).
Examples of non-metals are hydrogen H 2 oxygen O 2 and ozone O 3, nitrogen N 2, helium He, neon Ne, argon Ag, carbon C (such a joint reality is applied to all simple substances of Carbon), sulfur S, phosphorus P, chlorine Cl 2 , iodine I 2 and others (Fig. 58).
Among the chemical elements, metallic ones predominate. Of the chemical elements known today, only 22 are non-metallic.
In paragraphs 6 and 7, the main physical properties of substances were considered. Focusing on this, we will compose the characteristics of simple substances of metals and non-metals.
The common properties of all metals are high thermal and electrical conductivity; gray, silver gray (examples of exceptions: gold - yellow, copper - brick red); lack of smell; plasticity - they are easy to forge, draw into wire, roll into sheets. All metals at room temperature are in a solid state of aggregation, except for mercury (liquid).
These properties are not characteristic of non-metals. Therefore, we can say about them that they are simple substances that do not have metallic properties. So, non-metals do not conduct or poorly conduct heat and electric current, are brittle, and not ductile. Hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, fluorine, chlorine, helium, argon and others at room temperature are in a gaseous state of aggregation. Phosphorus, carbon, sulfur, iodine are solids, bromine is a liquid. Non-metals have more color differences than metals. So, oxygen and hydrogen are colorless, sulfur is yellow, chlorine is yellow-green, bromine is dark brown.
Rice. 57. Samples of metals: a - zinc; b - aluminum, c - iron, d - copper

Rice. 58. Samples of non-metals: a - iodine, sulfur, c - phosphorus, d - chlorine
It should be emphasized that the division of simple substances only by physical properties into metals and non-metals is inaccurate. For example, non-metal iodine has a metallic luster, and non-metal graphite is characterized by high electrical conductivity. In the next classes, you will expand your knowledge of the division of simple substances into metals and non-metals based on differences in the structure of their atoms and chemical properties.
PLACEMENT OF METALLIC AND NON-METALLIC ELEMENTS IN THE PERIODIC SYSTEM. Chemical elements, the atoms of which are formed by simple substances - metals, are called metallic, and chemical elements, the atoms of which are formed by simple substances - non-metals - non-metallic.
In paragraph 12, you first got acquainted with the periodic table of chemical elements. Now you know that the chemical elements are arranged with increasing charge of the nuclei of atoms, and that one cell is invariably assigned to each element. Is there any regularity in the placement of metallic and non-metallic elements in the periodic system? To answer this question, let's work with the table. Let's choose for consideration the 1st, 2nd and 3rd periods. In the first period, there are no metallic elements. The second period begins with the metallic element Li. The next element, Beryllium Be, also belongs to the metallic ones. The remaining elements of this period are non-metal.
The third period also begins with the metal element Sodium Na, after which two more metal elements are placed - Magnesium Mg and Aluminum Al. Further, as in the second period, non-metallic elements are placed.
Read aloud the names of the elements of the 1st, 2nd and 3rd periods.
Metallic and non-metallic elements are placed somewhat differently in the vertical columns of the table - groups, numbered with Roman numerals from i to VIII. So, all cells of groups i and II (except for the first one in the group) are filled with metal elements. Non-metallic elements are placed at the beginning of the remaining groups, and metallic elements at the end.
Find with the teacher and read aloud the names of non-metallic elements that begin III-VIII groups.
The considered examples illustrate general rule placement of metallic and non-metallic elements in periods and groups of the periodic system:
Metallic elements are placed in the periodic system of chemical elements of D. I. Mendeleev at the beginning of periods and at the end of groups, and non-metallic - at the end of periods and at the beginning of groups.
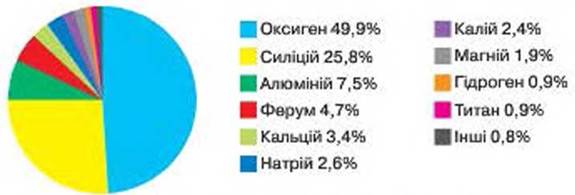
Rice. 59. Distribution of chemical elements on Earth (by mass)
DISTRIBUTION OF ELEMENTS IN NATURE. Although about 90 chemical elements are found in nature in the composition of various substances, they are distributed unevenly. There are leading elements, and there are those whose content is very small.
According to fig. 59 find out three metallic and three non-metallic elements are the most common on Earth. Do metallic or non-metallic chemical elements predominate in the composition of substances on planet Earth?
Piggy bank erudite
Among simple substances there are "champions" of various physical properties. So, diamond has the highest hardness, tungsten metal is the most refractory. Lithium is the lightest metal and hydrogen is the lightest non-metal. Among metals, silver, copper, and aluminum have the highest thermal conductivity. Bismuth and mercury have low thermal conductivity. Exist soft metals, which can be cut with a knife, for example, sodium, potassium, calcium, and chromium has the highest hardness among metals - they can cut glass. High ductility in gold. This makes it possible to produce a film of only 0.003 mm thick from it.
1. What substances are called simple? Give examples.
2. What groups are simple substances divided into? Which group has more representatives?
3. Name the general physical properties of metals.
4. What do you know about the arrangement of metallic and non-metallic elements in the periodic table?
5. What metal element begins the 4th period?
6. What non-metal element begins the V group?
7. Name three non-metallic and metallic chemical elements common on Earth.
8. From the list of chemical elements, select non-metallic ones and arrange them in order of increasing relative atomic mass: Magnesium, Oxygen, Hydrogen, Iron, Nitrogen, Chlorine.
9. Using the periodic table of chemical elements, name the chemical element placed in the 3rd period and the VIII group. Does it belong to metallic or non-metallic elements? How many protons and electrons are in its atom?
10. Fill in the gaps in the sentences with the words “metal”, “non-metal” and the names of the corresponding elements. The second period of the Periodic Table begins with _________ element _________, and ends with ________ element ___________.
The sixth group of the periodic system begins with the element _________, and ends with the element ________,
11. Indicate as many signs as possible, according to which the lists of simple substances are concluded:
a) oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen;
6) silver, iron, aluminum?
Complete a project on the topic "Chemical elements in the composition of various celestial bodies."









